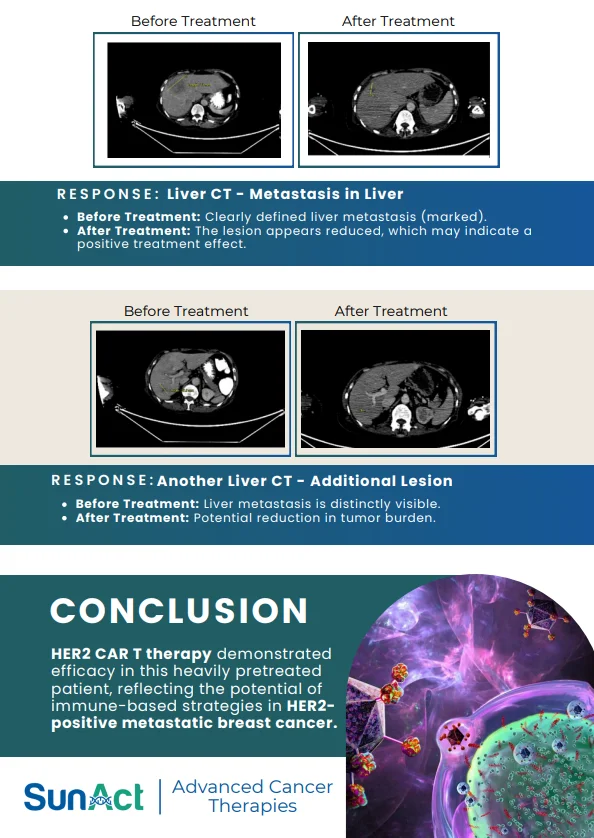
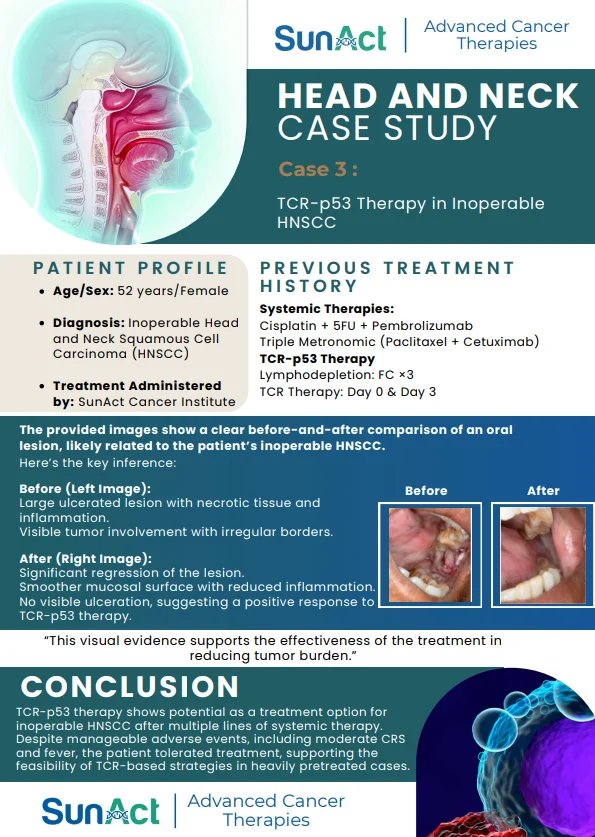
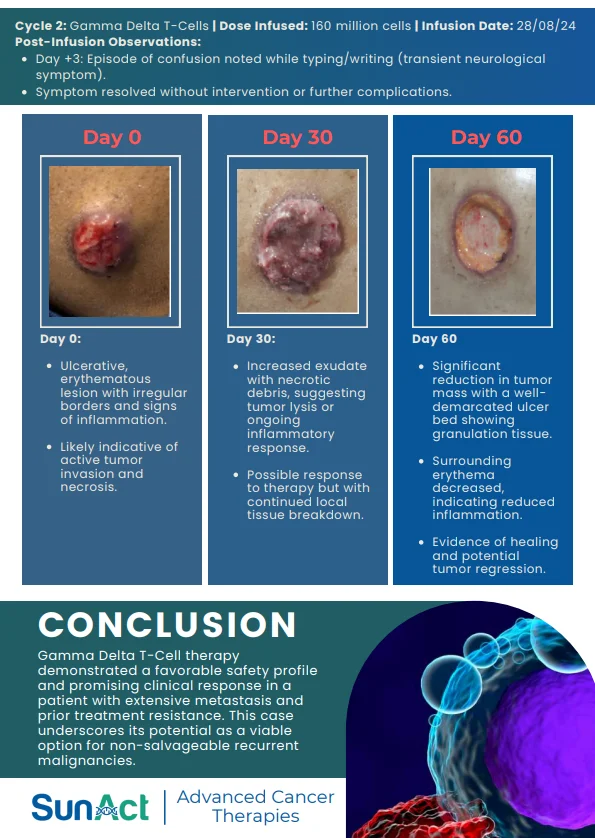
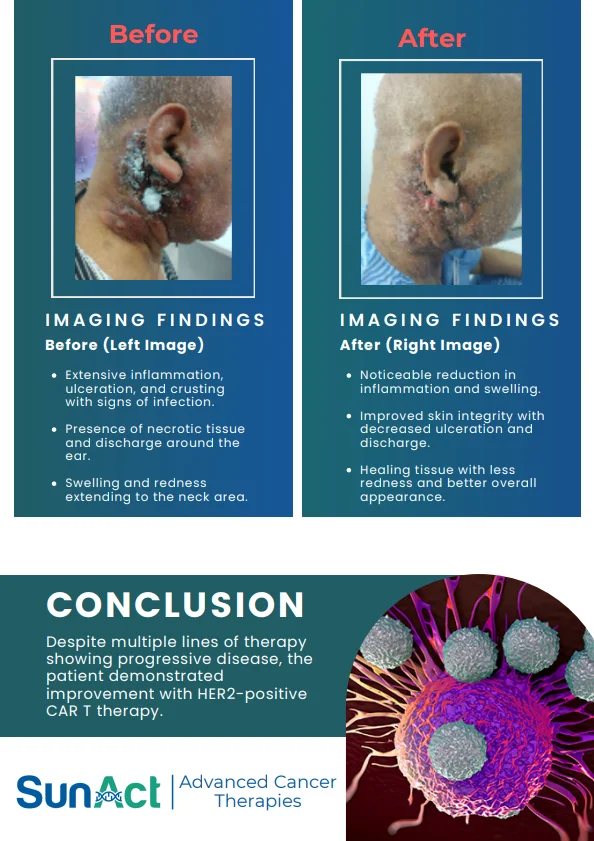
Potential Cure : Offers the possibility of curing certain cancers and blood disorders.

Immune System Rebuilding : Helps restore the immune system.

Broad Applicability : Can be used to treat a variety of cancers and blood-related conditions.
Source: Uses the patient’s own stem cells
Collection: Stem cells collected from the patient via peripheral blood or bone marrow
Conditioning: High-dose chemotherapy or radiation to eliminate diseased marrow
Infusion: Patient’s own stem cells are infused back
Engraftment: Stem cells migrate to bone marrow and regenerate blood cells
Risk of Rejection: Minimal, since cells are from the patient
Suitability: Best for patients needing high-dose chemo with stem cell rescue
Procedure Complexity: Moderate – involves collection, storage, and reinfusion of own cells
Common Uses: Lymphoma, Multiple Myeloma
Cost: Lower cost due to use of own cells
Success Factors: Dependent on patient health and disease sensitivity to chemo
Source: Uses stem cells from a healthy donor
Collection: Stem cells collected from a matched donor via peripheral blood or bone marrow
Conditioning: High-dose chemotherapy or radiation to prepare for donor cell engraftment
Infusion: Donor stem cells are infused into the patient
Engraftment: Donor cells engraft and rebuild the patient’s immune and blood system
Risk of Rejection: Higher risk, including Graft-Versus-Host Disease (GVHD)
Suitability: Ideal for patients with bone marrow failure or genetic blood disorders
Procedure Complexity: High – requires donor matching, immune suppression, and close monitoring
Common Uses: Leukemia, Aplastic Anemia, Thalassemia, Sickle Cell Anemia
Cost: Higher cost due to donor search, preparation, and long-term care
Success Factors: Dependent on donor match, patient health, and immune response