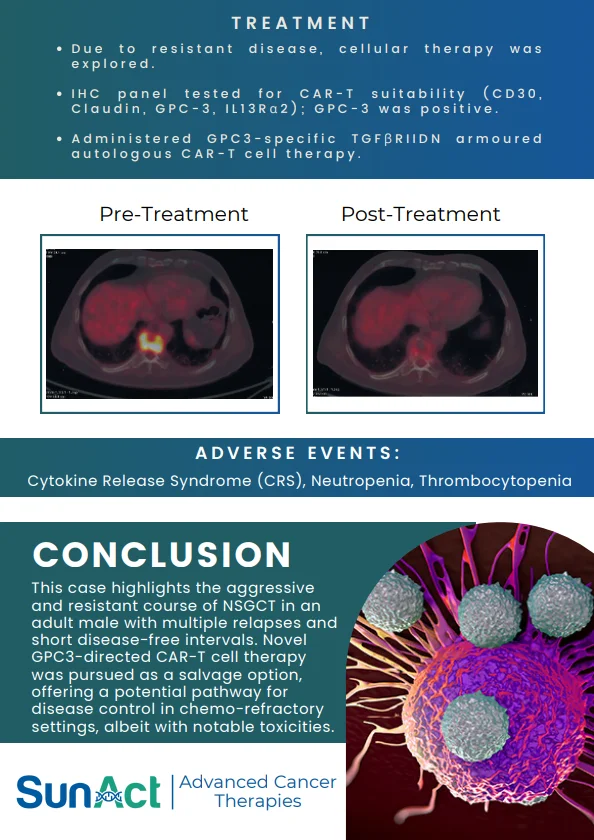
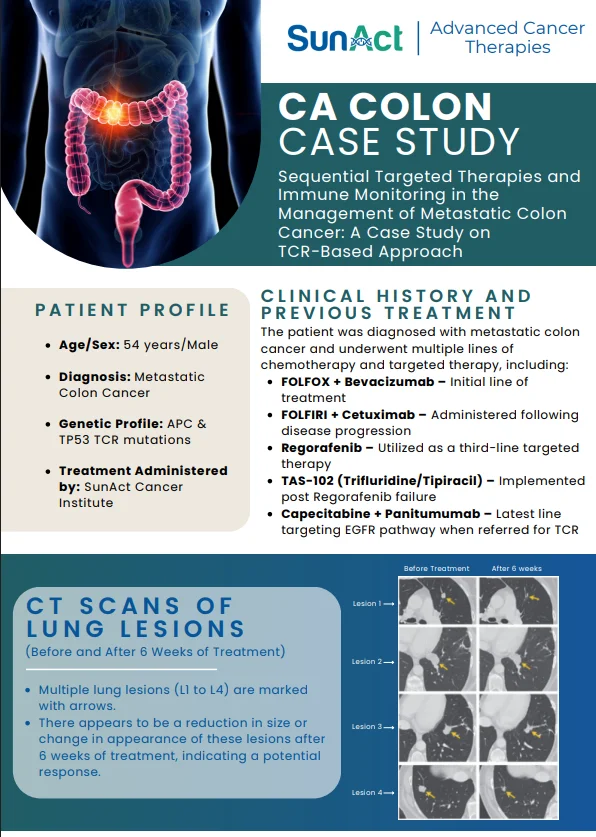
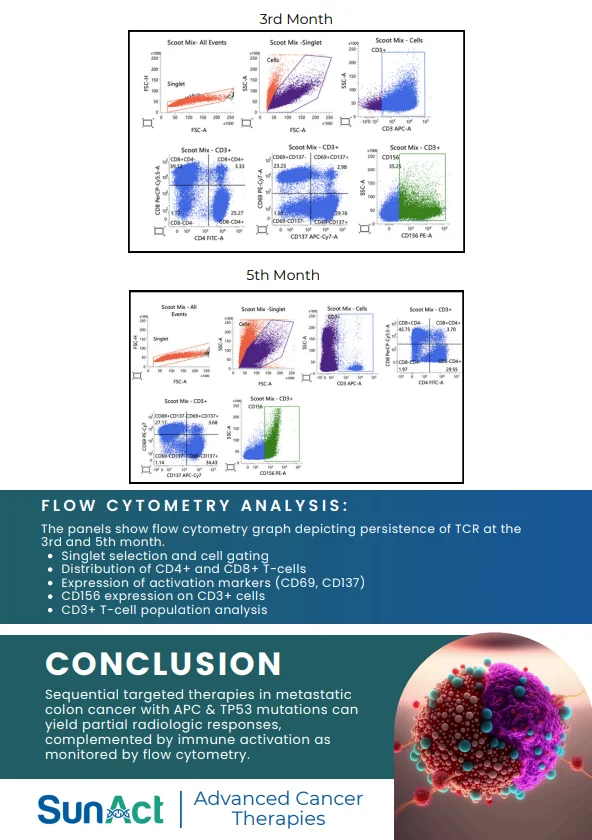
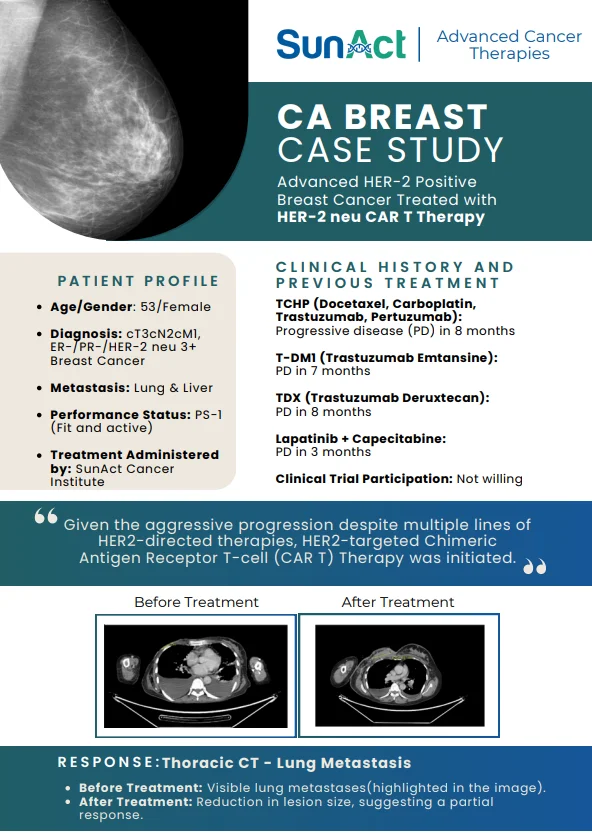
Chemotherapy is used to treat a wide range of cancers, including:

Shrinking Tumors: Can reduce the size of tumors before surgery or radiation therapy.

Curing Cancer: Can eliminate cancer cells completely, leading to a cure for some types of cancer.

Symptom Relief: Can help manage cancer-related symptoms, such as pain.

Preventing Recurrence: Used after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells and prevent the cancer from returning.
Adjuvant Chemotherapy
Description: Given after the primary treatment (like surgery) to destroy any remaining cancer cells
Common Uses: Breast cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer
Side Effects: Fatigue, hair loss, nausea
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Description: Given before the main treatment to shrink a tumor, making it easier to remove with surgery or radiation
Common Uses: Breast cancer, head and neck cancer
Side Effects: Nausea, vomiting, nerve damage
Palliative Chemotherapy
Description: Used to relieve symptoms and improve a patient’s quality of life when a cure is not possible
Common Uses: Advanced cancers
Side Effects: Fatigue, loss of appetite, mouth sores
Combination Chemotherapy
Description: Uses two or more drugs at the same time to increase effectiveness and reduce the likelihood of drug resistance
Common Uses: Lymphoma, leukemia
Side Effects: Side effects may be more pronounced
Patients undergo tests to ensure they are healthy enough for treatment. Doctors create a personalized treatment plan.
Treatment is often given in cycles, with a period of treatment followed by a period of rest to allow the body to recover.
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor recovery and check for any side effects or recurrence.