23 December 2025
Breast cancer is often perceived as a disease of older women, but an increasing number of cases are being diagnosed in women under the age of 40. Breast cancer in young women presents unique challenges, both in terms of diagnosis and treatment, making awareness and timely care especially important.
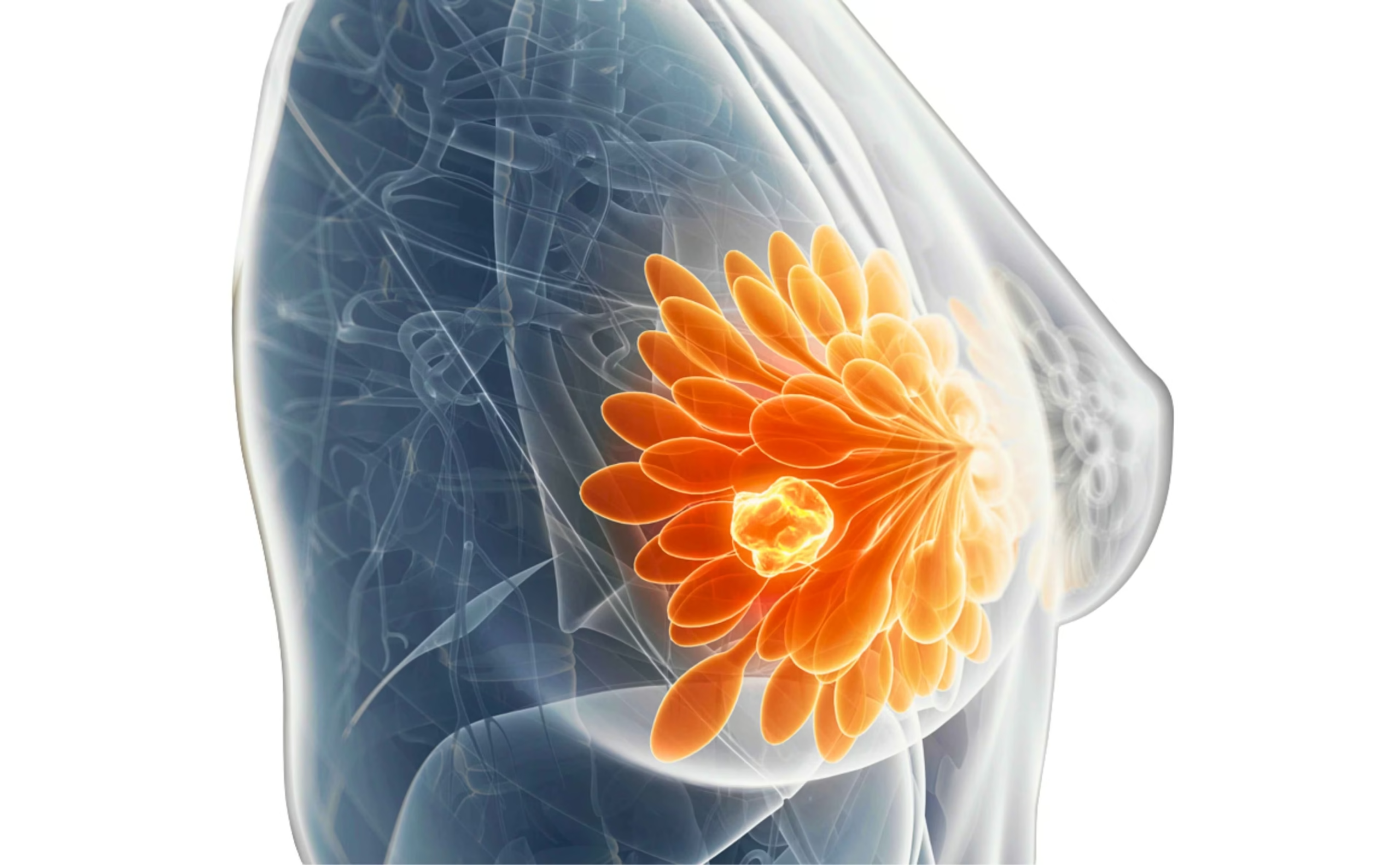
In younger women, breast tissue tends to be denser. This can make early tumors harder to detect on routine imaging and may delay diagnosis. Symptoms can also be subtle. Apart from a breast lump, warning signs may include persistent breast pain, nipple discharge, skin dimpling, changes in breast size or shape, or redness that does not resolve. Because many young women do not consider themselves at risk, these symptoms are sometimes ignored or attributed to hormonal changes.
Biologically, breast cancer in younger patients is often more aggressive. Higher rates of triple-negative and HER2-positive breast cancers are seen in this age group, which may require intensive and carefully planned treatment. Management usually involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation, or hormone therapy—tailored to the cancer type and stage.
An important consideration in young women is fertility preservation. Treatments such as chemotherapy can affect ovarian function. Early discussion about fertility options, including egg or embryo preservation, is a crucial part of care. Emotional and psychological support is equally important, as young patients often face concerns related to body image, career disruption, relationships, and future family planning.
Treatment decisions for young women with breast cancer are best made through a multidisciplinary approach that balances effective cancer control with quality of life, fertility preservation, and long-term health considerations.
Breast cancer at a young age can be overwhelming, but with early diagnosis, personalized treatment, and comprehensive support, outcomes can be excellent.
If you notice persistent breast changes at any age, early evaluation can make all the difference.