Welcome to the SunAct Cancer Research Insights Newsletter, your monthly update on global breakthroughs shaping the next generation of cancer and cell-based therapies.
In this issue, we explore pioneering advances in CGT/ACT therapy, advancement in detection methods, and regulatory fast-tracks that are accelerating access to life-changing treatments. Our goal is to keep clinicians and researchers informed about innovations redefining patient care worldwide.
Direct mRNA delivery via lipid nanoparticles enables in-body generation of CAR-T – cells targeting GPC3+ hepatocellular carcinoma, no cell harvesting, no lab expansion and just precision immunotherapy activated from within.
Delivers functional CAR T-cells without ex vivo cell manufacturing, enabling rapid deployment, reduced manufacturing burden, and targeted cytotoxicity against GPC3+ liver tumors, advancing accessibility in solid tumor immunotherapy.
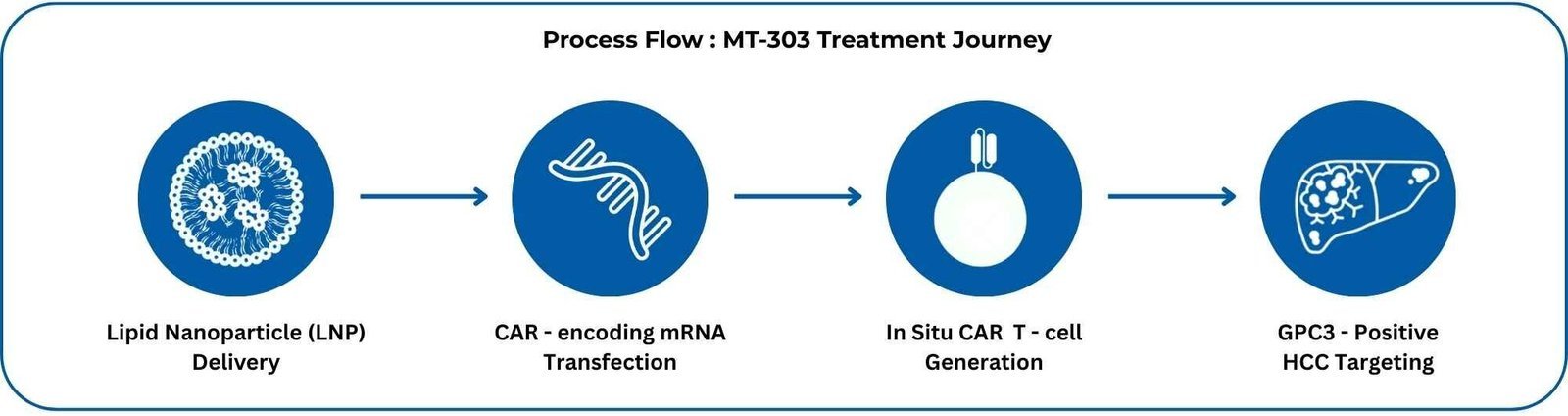
“Off-the-shelf” in-body–generated CAR-T could become a realistic option for GPC3+HCC—and eventually other solid tumors—reshaping referral pathways, eligibility timing, and sequencing of systemic therapies.
Novel CRISPR/Cas9-edited Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) with enhanced cytotoxicity, persistence, and resistance to immunosuppression within solid tumors have been developed.
This dual-editing strategy reprograms TILs to achieve deeper tumor infiltration and superior anti-tumor activity.
Improved Tumor Eradication: Enhanced cytotoxicity and antigen-specific killing in solid tumors.
Long-Term Therapeutic Activity: Extended TIL survival supports durable responses.
Wider Clinical Applicability: Enables TIL therapy beyond melanoma, with applicability to multiple solid tumor types.
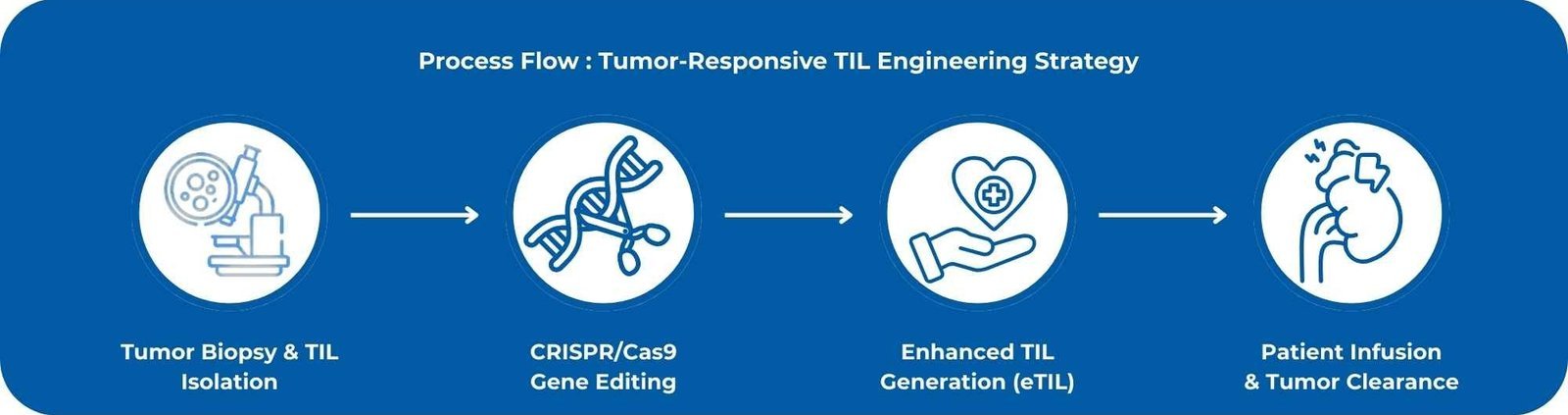
Identify and refer patients with solid tumors earlier for trials using CRISPR-optimized TILs, as these engineered products may significantly elevate the therapeutic ceiling of adoptive cell therapy in solid malignancies.
Blood-based liquid biopsy monitors circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) to assess CAR-T therapy effectiveness in lymphomas like DLBCL and follicular lymphoma. It detects minimal residual disease (MRD) and CAR-T persistence without tissue samples, using genomic and epigenomic markers, delivering results in ~7 days.
Recent 2025 data (Clinical Lymphoma Myeloma & Leukemia, August 2025; ASGCT 2025) shows MRD in 89% of cases and predicts progression-free survival with 85% accuracy, spotting relapse 3–6 months before imaging. Early intervention based on these insights may boost outcomes by 20–30%, with integration into CAR-T protocols underway (NCT05588094, targeting 2026).
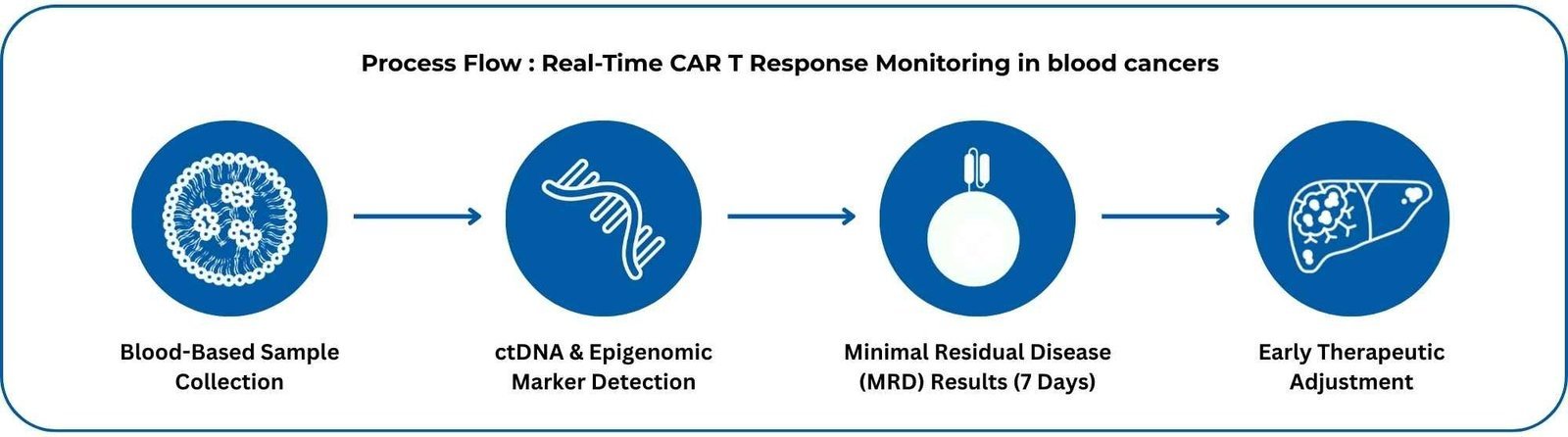
Plan to incorporate serial ctDNA MRD testing into lymphoma CAR-T follow-up to stratify relapse risk early and personalize post-infusion management.
Regulatory initiatives emphasise adaptive trial designs, clearer post‑approval frameworks and priority pathways to streamline CGT development.
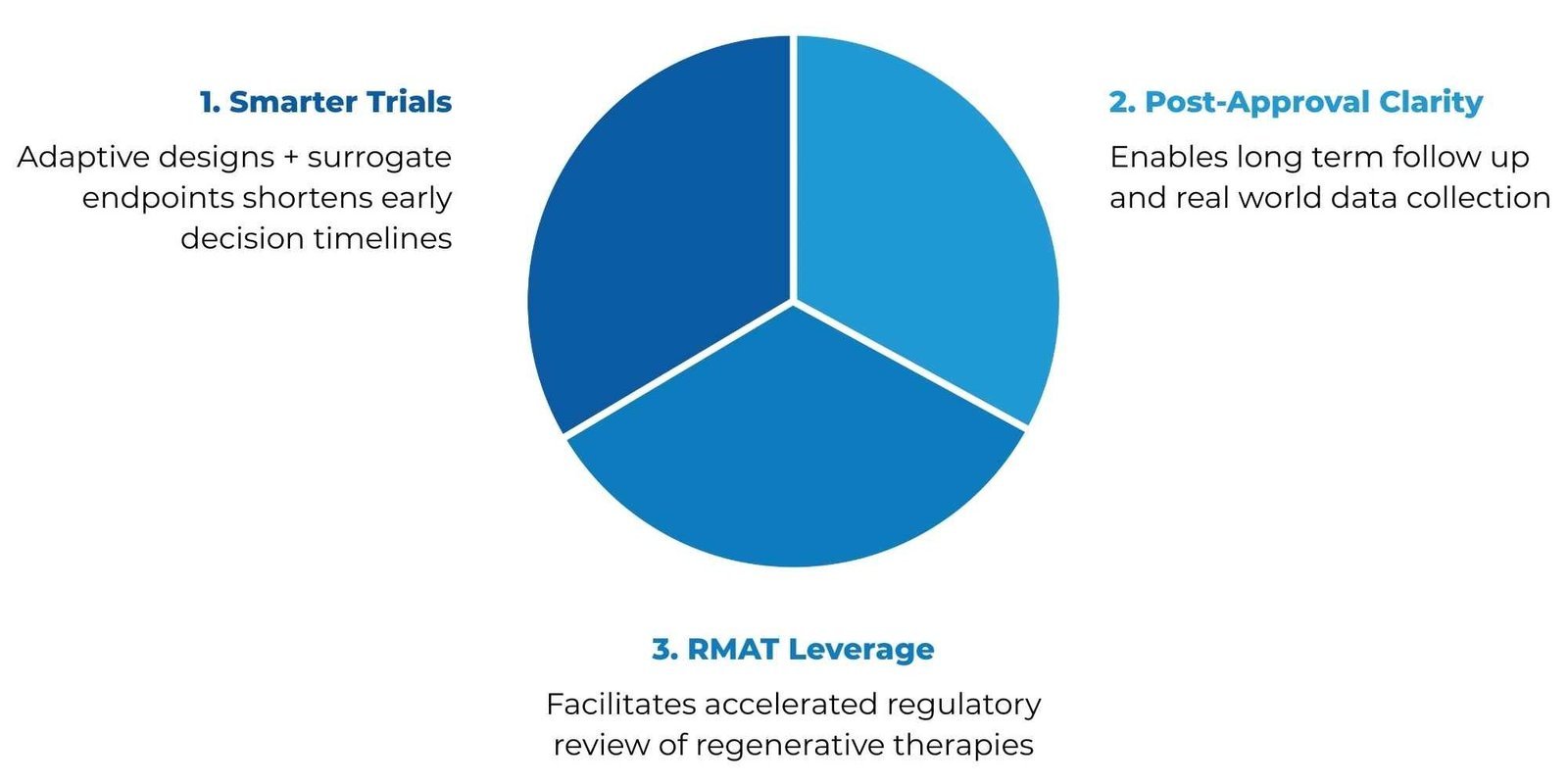
Smarter Trials: Adaptive designs and surrogate endpoints shorten timelines.
Post-Approval Clarity: Enables long-term follow-up and real-world data collection.
RMAT Leverage: Facilitates accelerated regulatory review of regenerative therapies.
These frameworks cut CGT development time by up to 50%, bringing rare disease therapies to patients faster, with smarter trials and real-world data.
Prepare for more rapid adoption of early-approved CGTs and ensure systems are in place for vigilant post-marketing surveillance and timely referral to adaptive trials.

At SunAct, we remain dedicated to tracking and sharing global advances that continue to redefine the landscape of cellular therapy and oncology. Stay tuned for our next edition as we uncover more breakthroughs and emerging trends shaping the future of cancer research.
Disclaimer: This newsletter is intended for healthcare professionals and researchers. Information is for educational purposes only.