3 December 2025
What Is Aplastic Anemia?
Aplastic anemia is a condition where your bone marrow stops working properly.
Because of this, the body cannot produce enough:
- Red blood cells (to carry oxygen)
- White blood cells (to fight infections)
- Platelets (to help blood clot)
This combination is called pancytopenia
When all three types are low, the body becomes weak, more prone to infections, and bruises easily.
Why Does It Happen? (Causes)
Aplastic anemia can occur due to several reasons, but in many people, the exact cause is unknown. Common causes include:
- Autoimmune attack
The immune system mistakenly attacks the bone marrow.
- Certain medications
Such as:
- Some antibiotics
- Painkillers
- Anti-seizure medicines
(These may rarely harm bone marrow)
- Viral infections
Viruses like hepatitis, Epstein–Barr, or parvovirus can affect bone marrow.
- Exposure to chemicals
Benzene (found in petrol and industrial environments) is a known risk.
- Radiation or chemotherapy
These treatments for cancer can temporarily damage bone marrow.
- Inherited conditions
Rare genetic disorders like Fanconi anemia can cause it from childhood.
What Are the Symptoms?
Symptoms are mainly due to low blood cells.
When red blood cells are low (anemia):
- Tiredness
- Weakness
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath
- Fast heartbeat
When white blood cells are low (low immunity):
- Frequent infections
- Fever
When platelets are low (bleeding problems):
- Easy bruising
- Nosebleeds
- Gum bleeding
- Heavy periods
- Tiny red spots on skin (called petechiae)
How Is Aplastic Anemia Diagnosed?
Doctors use several tests to confirm it:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Shows low levels of red cells, white cells, and platelets.
- Peripheral Smear
A drop of blood under a microscope.
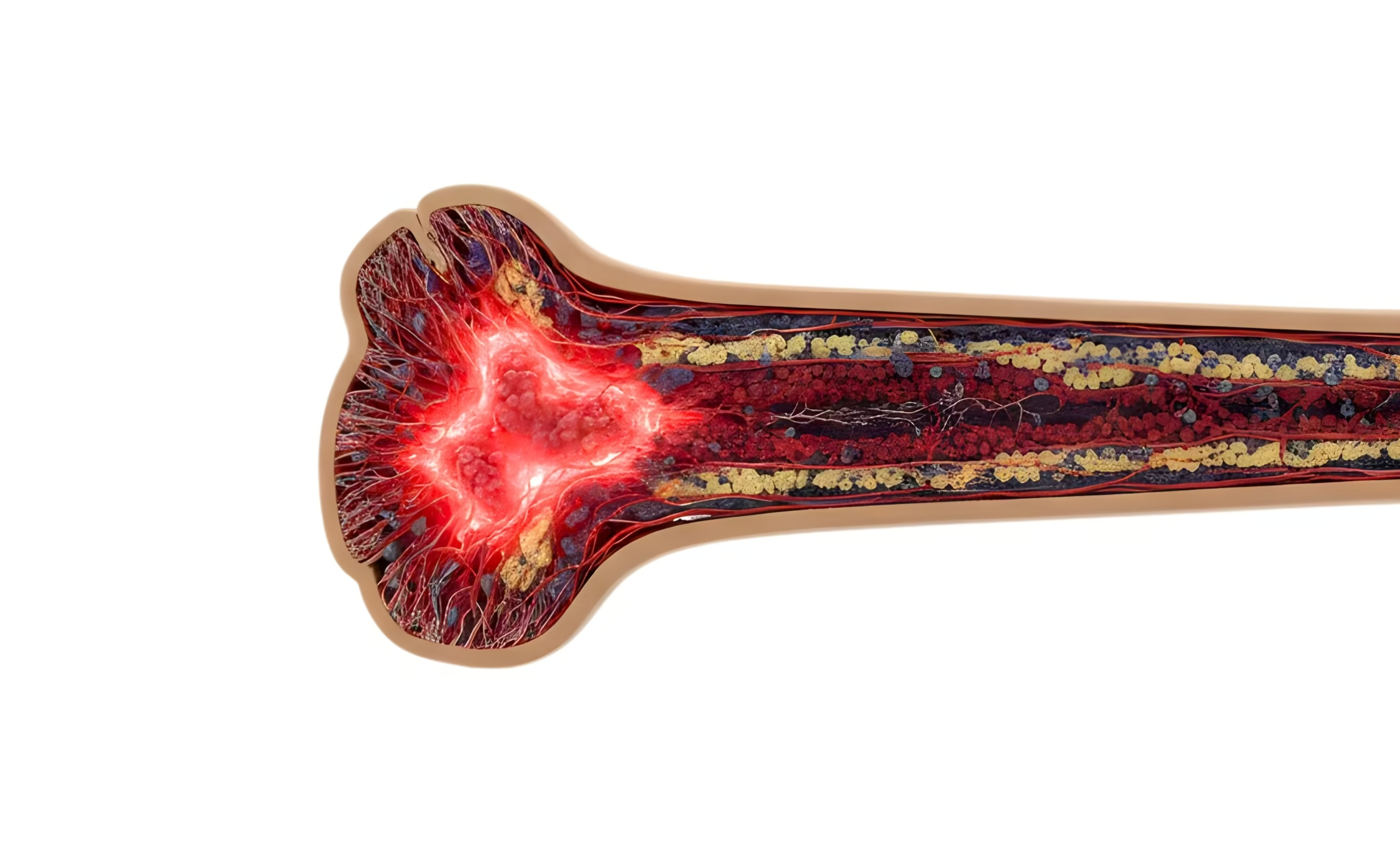
- Bone Marrow Biopsy
A small sample of bone marrow is taken (usually from the hip bone) to see if the marrow is empty or has very few cells.
- Viral tests & immune tests
To find the reason behind the condition.
How Is Aplastic Anemia Treated?
- Immunosuppressive Therapy (IST)
These medicines reduce the immune system’s attack on bone marrow. - Bone Marrow Transplant (Stem Cell Transplant)
Healthy stem cells (blood-forming cells) are taken from a donor and are given to the patient to rebuild the bone marrow. - Blood Transfusions
Used to temporarily improve symptoms:
Red cell transfusions for severe anemia
Platelet transfusions for bleeding risk. - Growth Factors
Medicines like G-CSF (Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor) help the bone marrow make more white blood cells.
Living With Aplastic Anemia
With proper treatment:
- Many patients recover well
- Some regain normal blood counts
- Some manage with long-term medications
- Regular follow-ups are important
Good hygiene, avoiding infections, and following doctor recommendations are key.
Conclusion
Aplastic anemia may be rare, but it is a condition that can be managed effectively with timely diagnosis, careful monitoring, and advanced treatment. With today’s medical therapies, from medications to stem cell transplantation most patients can expect meaningful improvement and a better quality of life.